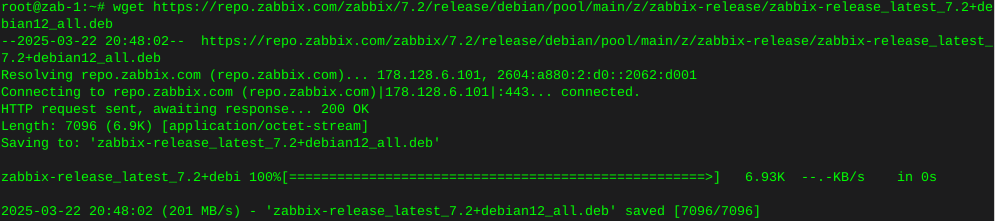
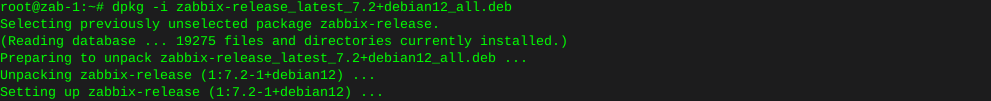
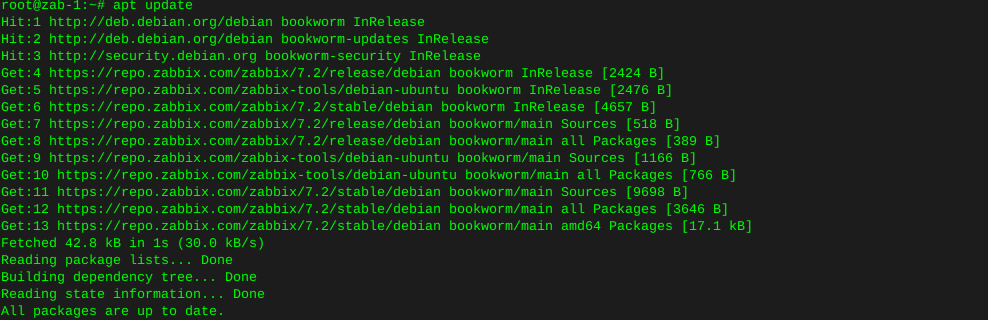
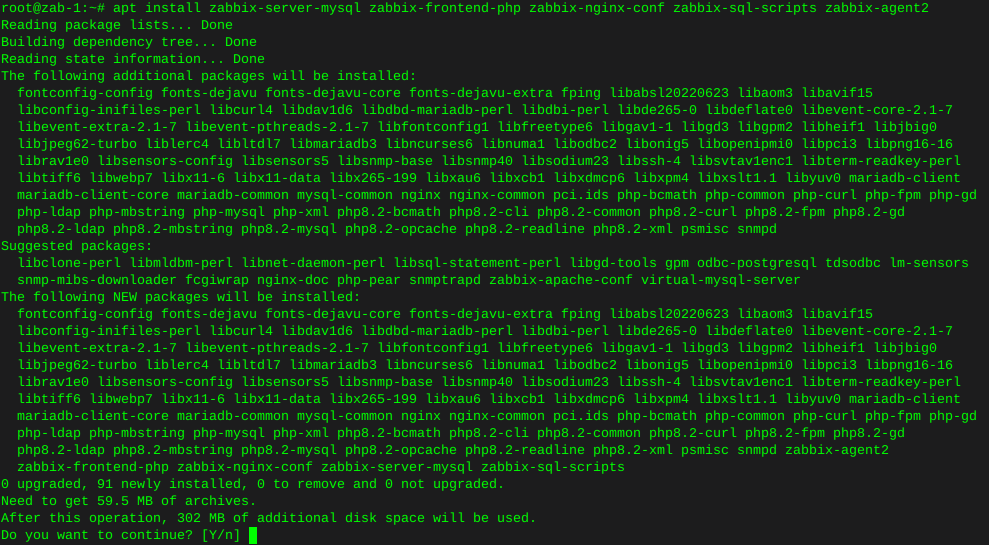
Locating files with the find command
-
Locating files using the find command
The find command is a powerful utility that allows the user to find files located in the file system via criteria such as the file name, when file was last accessed, when the file status was last changed, the file’s permissions, owner, group, size.
Find a file “foo.bar” that exists somewhere in the file system
find / -name foo.bar -printOn most platforms the -print is optional, however, on some systems nothing will be output without it. Without specifications find searches recursively through all directories.
Find a file without searching network or mounted file systems
find / -name foo.bar -print -xdevThis is useful if you have network drives that you know the file would not be located on. “-mount” does the same thing as “-xdev” for compatibility with other versions of find.
Find a file without showing “Permission Denied” messages
find / -name foo.bar -print 2>/dev/nullWhen find tries to search a directory or file that you do not have permission to read the message “Permission Denied” will be output to the screen. The 2>/dev/null option sends these messages to /dev/null so that the found files are easily viewed.
Find a file, who’s name ends with .bar, within the current directory and only search 2 directories deep
find . -name *.bar -maxdepth 2 -print
Search directories “./dir1” and “./dir2” for a file "foo.bar
find ./dir1 ./dir2 -name foo.bar -print
Search for files that are owned by the user “skippie”
find /some/directory -user skippie -printThe files output will belong to the user “skippie”. Similar criteria are -uid to search for a user by their numerical id, -group to search by a group name, and -gid to search by a group id number.
Find a file that is a certain type. “-type l” searches for symbolic links
find /any/directory -type l -print
Several types of files can be searched for: Several types of files can be searched for:
-
b block (buffered) special
-
c character (unbuffered) special
-
d directory
-
p named pipe (FIFO)
-
f regular file
-
l symbolic link
-
s socket
Search for directories that contain the phrase “foo” but do not end in “.bar”
find . -name '*foo*' ! -name '*.bar' -type d -printThe “!” allows you to exclude results that contain the phrases following it.
find becomes extremely useful when combined with other commands. One such combination would be using find and grep together.
find ~/documents -type f -name '*.txt' \ -exec grep -s DOGS {} \; -print -