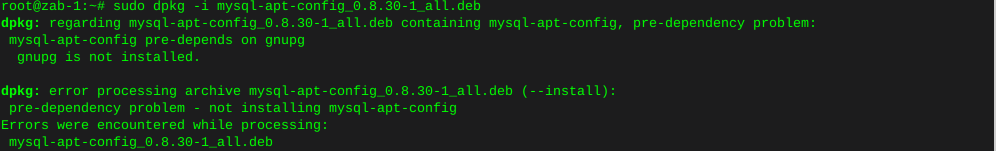
Burn ISO to cd/DVD/BD linux command line
-
There are still those times when {place whatever issue or project here} will require burning optical media, even a CD if you enjoy toying around with older, even ancient hardware.
That said there are many GUI programs which can accomplish this. However that’s not always viable, or desired. Especially when you care more about the command line and keeping your brain from going sedentary, by constantly clicking a button and having something done for you. /snarky
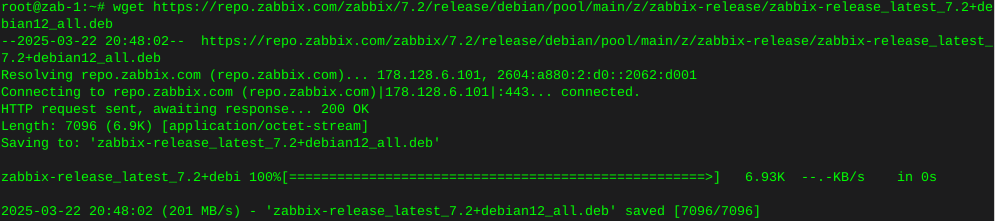
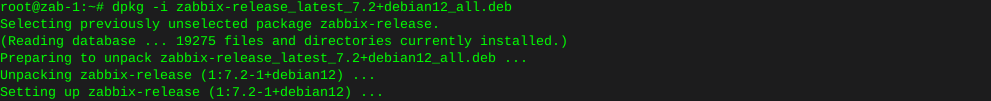
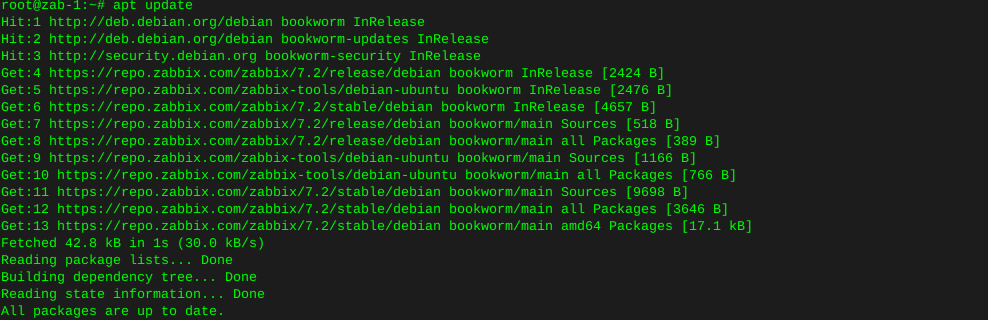
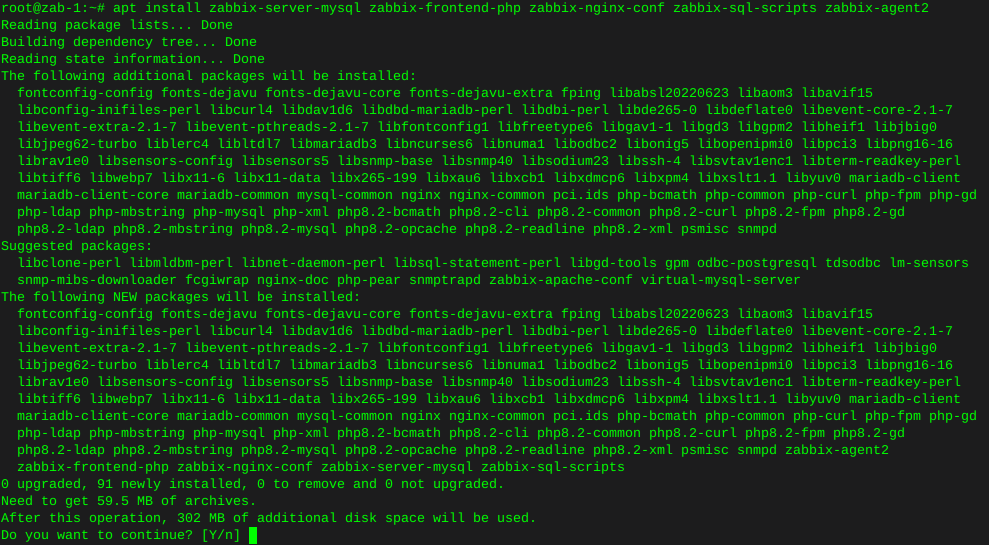
In this instance I’ll burn an ISO image of hdat2 to a cd from the command line using wodim on Debian.
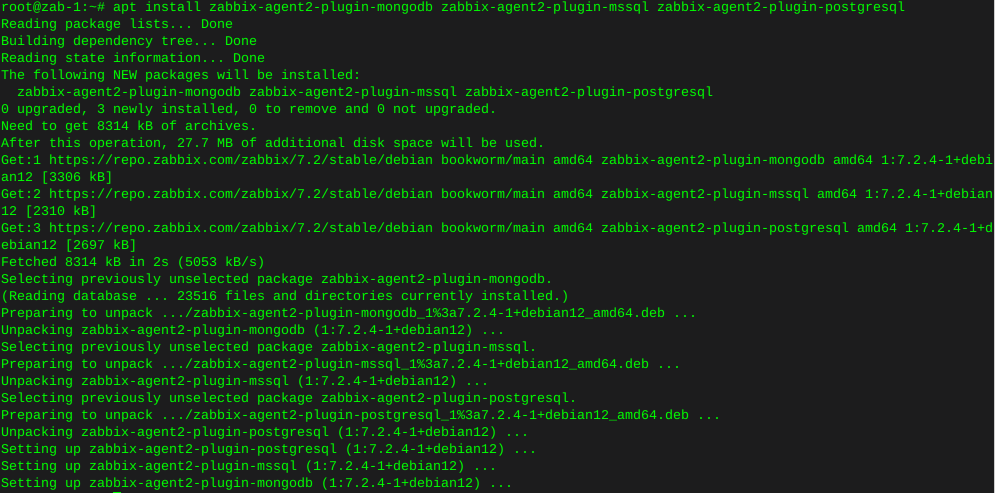
Install wodim:
sudo apt-get install wodim
Burn ISO to a cd:
Find the drive name in which you will use to write the image: You can have a quick look at how to burn an ISO to USB which contains the same basic procedure for locating storage devices locally. Or continue on.
Locate the device which you intend to use to burn by using the command:
lsblkIn this case the output is as follows:
rick@deb:~$ lsblk NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT sda 8:0 0 465.8G 0 disk └─isw_ccheigfjba_Volume0 254:0 0 931.5G 0 dmraid ├─isw_ccheigfjba_Volume01 254:1 0 893.8G 0 dmraid / └─isw_ccheigfjba_Volume05 254:2 0 37.7G 0 dmraid sdb 8:16 0 465.8G 0 disk └─isw_ccheigfjba_Volume0 254:0 0 931.5G 0 dmraid ├─isw_ccheigfjba_Volume01 254:1 0 893.8G 0 dmraid / └─isw_ccheigfjba_Volume05 254:2 0 37.7G 0 dmraid sdc 8:32 0 2T 0 diskThis shows two disks (sda & sdb) in raid form, as well as the optical device we will use (SDC)
Next, Navigate to the directory of the ISO (not required but simplifies the command) many times in the downloads directory.
Now we are ready to burn the ISO to cd.
Type the following in command line:
wodim -v dev=/dev/sr0 -eject -sao hdat2cd_51.isoHere is the output after hitting return:
TOC Type: 1 = CD-ROM scsidev: '/dev/sr0' devname: '/dev/sr0' scsibus: -2 target: -2 lun: -2 Linux sg driver version: 3.5.27 Wodim version: 1.1.11 SCSI buffer size: 64512 Device type : Removable CD-ROM Version : 0 Response Format: 3 Capabilities : Vendor_info : 'ATAPI ' Identification : 'iHAS324 A ' Revision : 'BL1A' Device seems to be: Generic mmc2 DVD-R/DVD-RW. Current: 0x000A (CD-RW) Profile: 0x002B (DVD+R/DL) Profile: 0x001B (DVD+R) Profile: 0x001A (DVD+RW) Profile: 0x0016 (DVD-R/DL layer jump recording) Profile: 0x0015 (DVD-R/DL sequential recording) Profile: 0x0014 (DVD-RW sequential recording) Profile: 0x0013 (DVD-RW restricted overwrite) Profile: 0x0012 (DVD-RAM) Profile: 0x0011 (DVD-R sequential recording) Profile: 0x0010 (DVD-ROM) Profile: 0x000A (CD-RW) (current) Profile: 0x0009 (CD-R) Profile: 0x0008 (CD-ROM) Profile: 0x0002 (Removable disk) Using generic SCSI-3/mmc CD-R/CD-RW driver (mmc_cdr). Driver flags : MMC-3 SWABAUDIO BURNFREE FORCESPEED Supported modes: TAO PACKET SAO SAO/R96P SAO/R96R RAW/R16 RAW/R96P RAW/R96R Drive buf size : 1275648 = 1245 KB Beginning DMA speed test. Set CDR_NODMATEST environment variable if device communication breaks or freezes immediately after that. FIFO size : 12582912 = 12288 KB Track 01: data 13 MB Total size: 15 MB (01:34.97) = 7123 sectors Lout start: 16 MB (01:36/73) = 7123 sectors Current Secsize: 2048 ATIP info from disk: Indicated writing power: 3 Reference speed: 6 Is not unrestricted Is erasable Disk sub type: High speed Rewritable (CAV) media (1) ATIP start of lead in: -11745 (97:25/30) ATIP start of lead out: 359848 (79:59/73) 1T speed low: 4 1T speed high: 10 2T speed low: 4 2T speed high: 0 (reserved val 6) power mult factor: 1 5 recommended erase/write power: 5 A1 values: 24 1A D8 A2 values: 26 B2 4A Disk type: Phase change Manuf. index: 40 Manufacturer: INFODISC Technology Co., Ltd. Blocks total: 359848 Blocks current: 359848 Blocks remaining: 352725 Forcespeed is OFF. Speed set to 1765 KB/s Starting to write CD/DVD at speed 10.0 in real SAO mode for single session. Last chance to quit, starting real write in 0 seconds. Operation starts. Waiting for reader process to fill input buffer ... input buffer ready. Performing OPC... Sending CUE sheet... Writing pregap for track 1 at -150 Starting new track at sector: 0 Track 01: 13 of 13 MB written (fifo 100%) [buf 100%] 10.6x. Track 01: Total bytes read/written: 14587904/14587904 (7123 sectors). Writing time: 27.528s Average write speed 3.9x. Min drive buffer fill was 100% Fixating... Fixating time: 17.593s BURN-Free was never needed. wodim: fifo had 230 puts and 230 gets. wodim: fifo was 0 times empty and 30 times full, min fill was 96%.As you can see, the -v flag (verbose) allows us to get a bit more data as the process is happening. Of course this particular image was only ~15MB, so the time was very short, larger images will of course take much longer.
The burner door will open when the process is complete.
To burn a DVD via command line : We’ll use a script called growisofs:
sudo apt-get install growisofsFollow the same procedure to locate the proper device using the command:
lsblkMove to the directory the ISO is located, and type:
growisofs -dvd-compat -Z /dev/sr0=hdat2cd_51.isoFin